Joint Health Condition Utility Methods
Common methods used to estimate Utility
- Additive method
- Multiplicative method
- Minimum method
- Adjusted decrement estimator
- Combination model (Linear index)
Ara R, Wailoo AJ. Estimating Health State Utility Values for Joint Health Conditions: A Conceptual Review and Critique of the Current Evidence. Med Decis Making. 2013;33(2):139–153.
1. Additive Method
Idea: Individual disutilities are summed.
U_{A,B} = 1 - \big[(1-U_A) + (1-U_B)\big] = U_A + U_B - 1
Example:
- U_{\text{Stroke}} = 0.68
- U_{\text{AD}} = 0.54
U_{\text{Stroke, AD}} = 0.68 + 0.54 - 1 = \mathbf{0.22}
2. Multiplicative Method
Idea: Individual utility values are multiplied.
U_{A,B} = U_A \times U_B
Example:
- U_{\text{Stroke}} = 0.68
- U_{\text{AD}} = 0.54
U_{\text{Stroke, AD}} = 0.68 \times 0.54 = \mathbf{0.3672}
3. Minimum Method
Idea: Select the lower (minimum) of the component utilities.
U_{A,B} = \min(U_A, U_B)
Example:
- U_{\text{Stroke}} = 0.68
- U_{\text{AD}} = 0.54
U_{\text{Stroke, AD}} = \min(0.68, 0.54) = \mathbf{0.54}
4. Adjusted Decrement Estimator (ADE)
Combination of additive, multiplicative, and minimum methods using an adjustment factor.
Assumes the upper bound of U(A,B) equals \min(U_A, U_B).
U_{A,B} = \min(U_A, U_B) - \min(U_A, U_B)\times\big[(1-U_A)\times(1-U_B)\big]
Example:
- U_{\text{Stroke}} = 0.68
- U_{\text{AD}} = 0.54
U_{\text{Stroke, AD}} = 0.54 - 0.54\times\big[(1-0.68)\times(1-0.54)\big] = \mathbf{0.46}
5. Combination Model (Linear Index)
Parametric regression that assigns weights to elements from additive, multiplicative, and minimum structures.
\begin{aligned} U_{A,B} &= 1 - \Big[\beta_0 + \beta_1\,\min(1-U_A,\,1-U_B)\\ &\quad + \beta_2\,\max(1-U_A,\,1-U_B) + \beta_3\,(1-U_A)(1-U_B)\Big] + \epsilon \end{aligned}
Special cases:
- \beta_0=0,\;\beta_1=1,\;\beta_2=1,\;\beta_3=0 → Additive
- \beta_0=0,\;\beta_1=1,\;\beta_2=1,\;\beta_3=-1 → Multiplicative
- \beta_0=0,\;\beta_1=1,\;\beta_2=0,\;\beta_3=0 → Minimum
Requires observational data to estimate the \beta coefficients.
Performance comparison across methods
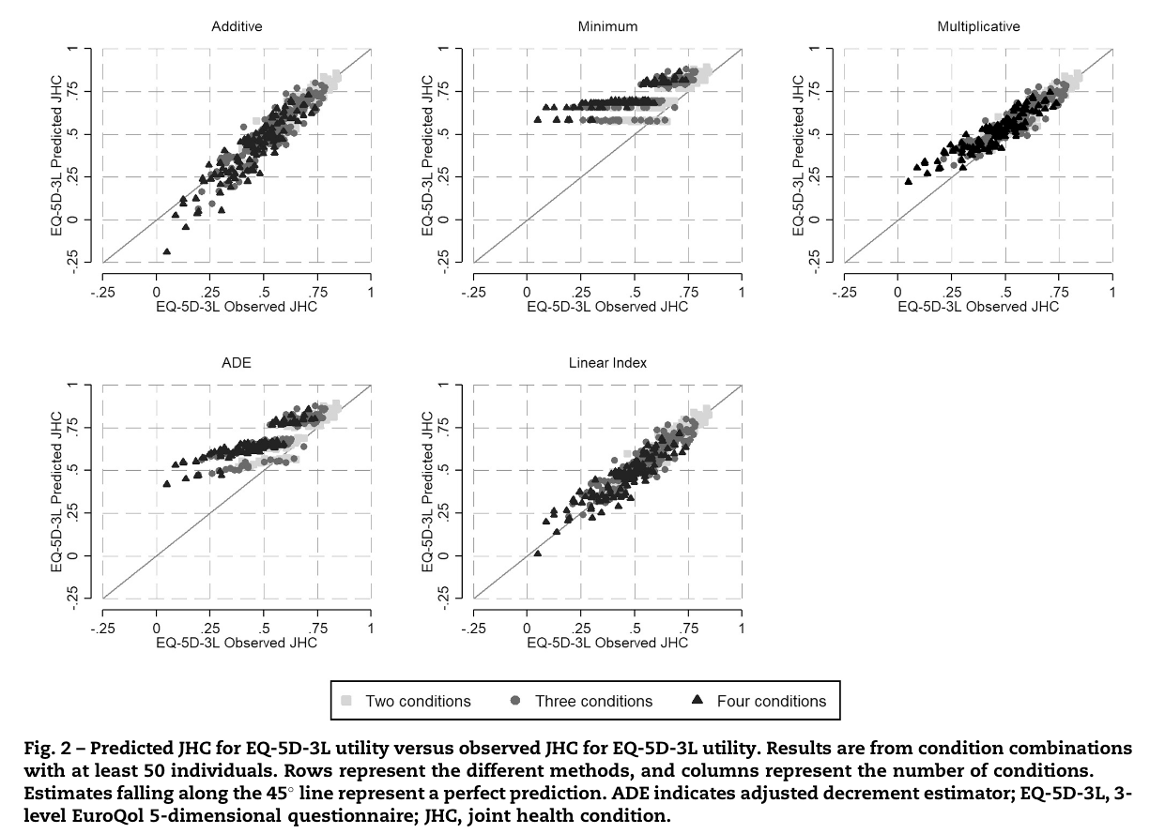
U_{\text{add, Stroke+AD}} = \mathbf{0.22}
U_{\text{multiply, Stroke+AD}} = \mathbf{0.3672}
U_{\text{min, Stroke+AD}} = \mathbf{0.54}
U_{\text{ADE, Stroke+AD}} = \mathbf{0.46}
Thompson AJ, Sutton M, Payne K. Estimating Joint Health Condition Utility Values. Value in Health. 2019;22(4):482–490.
