Case Study: QALYs
Decision Trees
Add QALY Dimension
We now want to add a new outcome dimension: QALYs (Quality-Adjusted Life Years). QALYs are a measure of disease burden, where 1 = perfect health and 0 = death.
Instructions:
In Amua, go to Model → Properties → Analysis tab.
Add a new dimension:
Dimension: QALE
Symbol: Q
Decimals: 2
Click
 Refresh
RefreshFor QALYs make sure the objective is maximizing
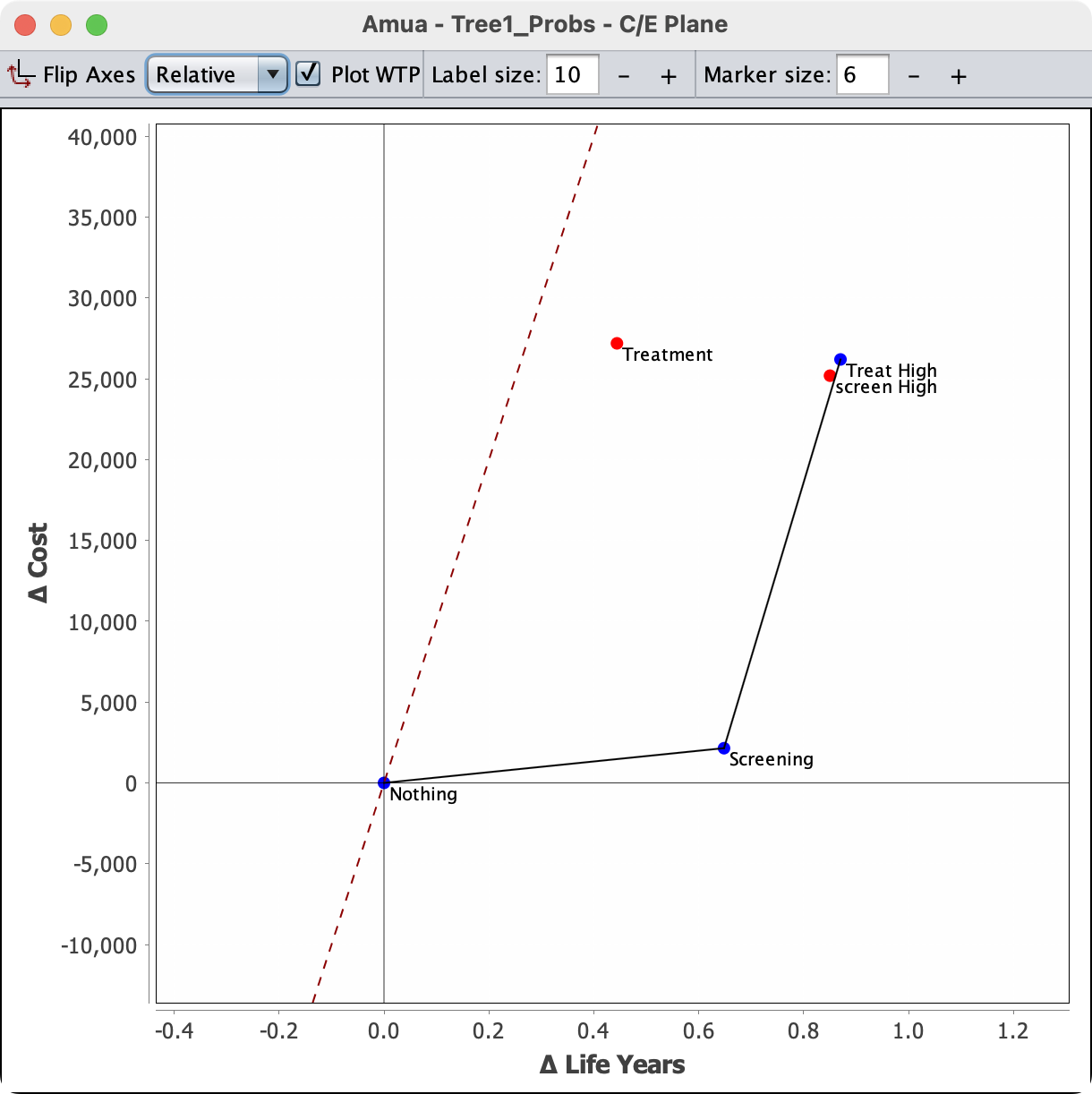
We can now return to the tree and enter QALE values at each terminal node
| Clinical State | QALE | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| QALE_Untreated | 3.21 | Large amounts of time at low quality of life |
| QALE_SickTreated | 14.54 | Short amounts of time sick and in treatment |
| QALE_Healthy | 20 | Full Health |
| QALE_HealthyTreated | 19.432 | Very short amount of time in treatment |
You can apply these QALE values to terminal nodes in Amua accordingly. Your tree should like this:
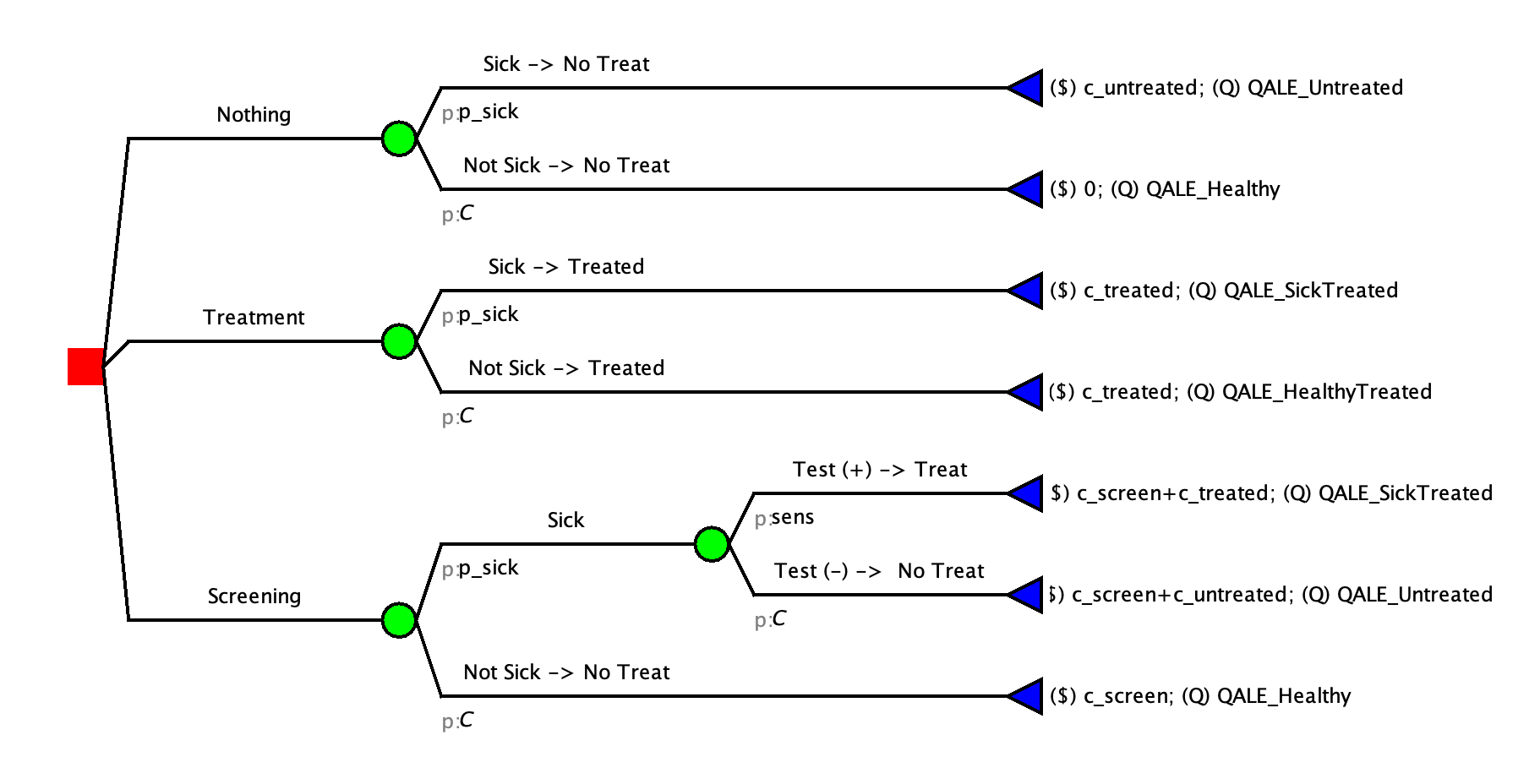
Now, you’re ready to perform a cost-effectiveness analysis with QALYs as the outcome!
Click  Run Model and check out the CEA Results report.
Run Model and check out the CEA Results report.
Markov Models
Add a DALY Dimension
We now want to add a new outcome dimension: DALYs (Disability-Adjusted Life Years). DALYs are a measure of disease burden, where 0 = perfect health and 1 = death per year lost. For this model, we will add Years of Life Lost. To discount these from the start of time and the time of occurrence we will use the built in discounting (from start time) and add discounting from the time of death.
To save time, we will go through the No Treat branch. A full answer key will be included at the end
A: Important Parameters
Quality of Life Adjustments
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| u_healthy | 1.0 | Quality-of-life (QoL) weight for healthy state. |
| u_sick | 0.842 | Quality-of-life (QoL) weight for sick health state. |
| u_sick_treated | 0.87 | Quality-of-life (QoL) weight for sick health state if treated. |
| u_dead | 0 | Quality-of-life (QoL) weight for death health states. |
Add QALYs
A: Add A DALY Outcome
In Amua, go to Model → Properties → Analysis tab.
Add a new dimension:
Dimension: DALYs
Symbol: D
Decimals: 2
Click
 Refresh
RefreshBecause DALY is a gap measure, change the objective to minimize DALYs (analogous to maximizing QALYs)
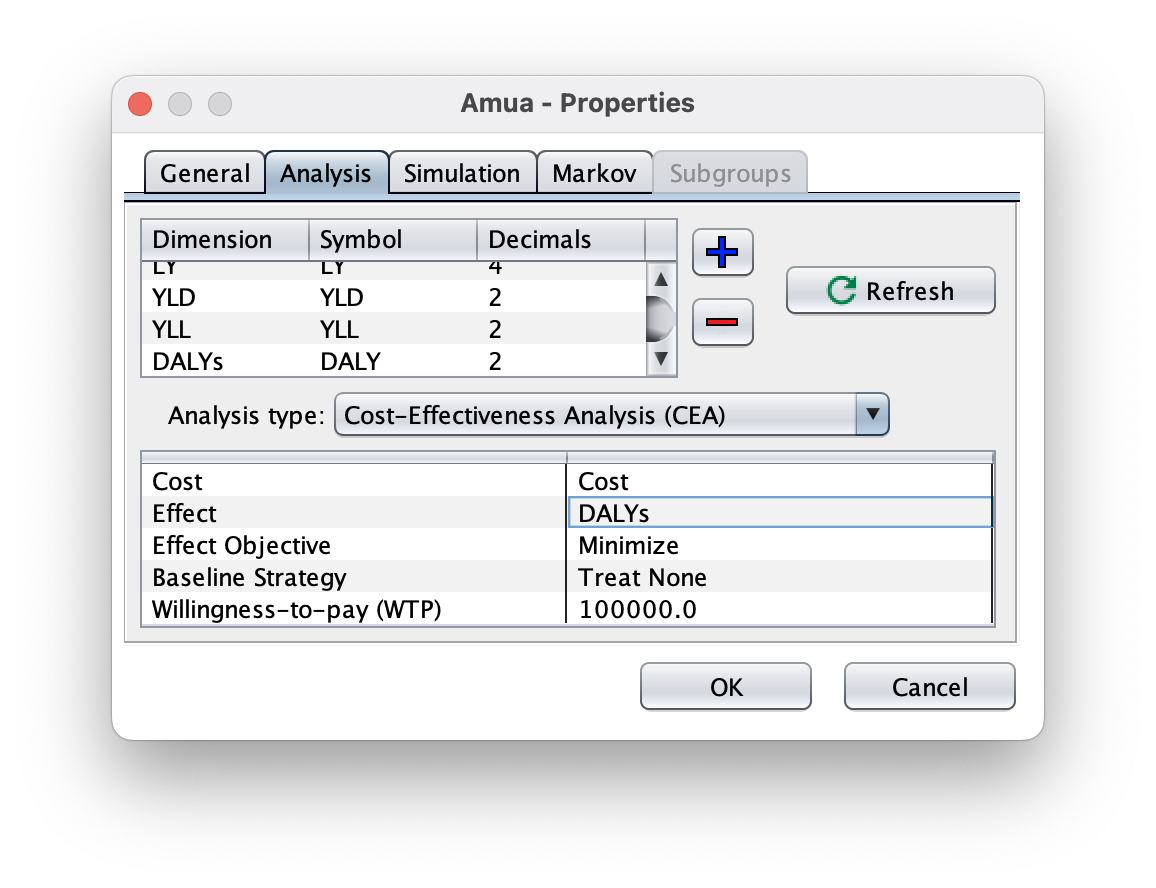
Add Outcome
Go to Model Properties select the Analysis tab.
Click the blue plus sign (
 ) to add a new outcome. Add DALYs.
) to add a new outcome. Add DALYs.Click the refresh button
Change the “Analysis Type” to Cost-Effectiveness Analysis (CEA).
Set the Cost, Effect, Baseline Strategy and Willingness-to-pay (WTP). Ensure that the Effect Objective is still set to minimize.
Go to the Markov tab and add in the discount rate for DALYs. (3.0)

Next, in the model itself, define the cycle-specific payoffs based on the values in the tables above.
- Every place in the model where there is a value for YLD or YLL, we will put that in DALYs so that it sums them all together.
- For Example: Under sick where it now has($) c_sick; (YLD) dw_sick ; (YLL) 0, we will have ($) c_sick; (YLD) dw_sick ; (YLL) 0 ; (DALY) dw_sick
- Every place in the model where there is a value for YLD or YLL, we will put that in DALYs so that it sums them all together.
Solution File: ADD FILE
What if there are multiple disability weights in one state?
For Example: You may get a disability weight for being sick and for a reaction to medication.
There are multiple ways to handle this: Joint Utility Methods Slides